
Untitled (Point Break), 2010, Roe Ethridge, via andrewkreps
This is in Le Luxe, Roe Ethridge’s awesome show at Kreps, through July 3rd.
Related: Crafting Genre: Kathryn Bigelow, a retrospective of the director’s film titles, combined with her early videos, paintings and conceptual artworks, opens at MoMA at the end of May. Point Break will be screening twice in early June, and once in August. [see the complete schedule.]
Category: movies
The Satelloons Of Buckminster Fuller
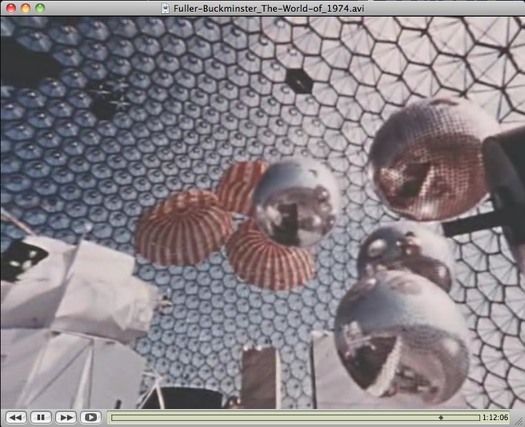
You know, every once in a while, I think that it’s crazy to be considering satelloons as art instead of what they really were–aestheticized objects designed to be seen and exhibited.
And then I’ll catch a glimpse of Expo 67 somewhere, and realize I’m still well inside the bubble.
A still from The World of Buckminster Fuller, which is on DVD, available at Amazon, not ubu.com, why would it be?
Previous Expo67 posts:
not that anyone asked, but here’s Fuller’s own idea for the US Pavilion
on the American Painting Now show, organized by Alan Solomon
the Canadian fracas over Barnett Newman’s Voice of Fire
Forgot how much I loved writing this post on art protestor/greenhouse owner John Czupryniak’s Newman knockoff, Voice of the Taxpayer
Expo 70 design finding the Expo 67 Pavilion hard to beat
The Global Puppy On Terror

In reviewing Johan Grimonperez’ 1997 film, Dial H.I.S.T.O.R.Y., which was exhibited at Deitch, Ronald Jones underscores artists’ failure to, well, to matter very much in contemporary culture. And he reminded me of this, which I had completely forgotten:
Paul Goldberger’s piece in the New Yorker on Frank Gehry’s Bilbao museum made an important claim: ‘The politics of the Guggenheim Bilbao’, Goldberger writes, ‘are evident in a single word, “MUSEOA”, that is plastered onto the building’s facade in enormous letters’. Goldberger’s point is that, ‘museoa’ is not Spanish but means ‘museum’ in the language of the Basques. We take from the Goldberger essay that a collision between art and politics was inevitable in Bilbao. As a part of the Bilbao Pageantry Jeff Koons’ well known Puppy (1992), the floral sculpture that made its magnificent debut in Kassel a few years ago, was to be erected and brought to life with local flowers. Languidly watching workmen hang pots of flowers over the gigantic pup, the police ran a casual check on the license plate of the truck which had been used to deliver the flowers. The truck and plate did not belong together and that’s how the terrorists were found out. When the police began nosing around they discovered that the ‘gardeners’ were arming the adorable puppy with flower pots containing remote-controlled grenades. After the shoot out, in which one policeman was killed, the florist-bombers, members of the Basque group ETA, escaped. Several have since been arrested.
[via frieze]
Related: Felix Gonzalez-Torres on politics and art
At The Movies With Mao Zedong
Tom Scocca posted about the story just before Christmas, but apparently, Mao Zedong was a Bruce Lee fan.
That’s how the Chinese press is reporting the story of Liu Qingtang, [刘庆棠], a ballet dancer and close ally of Mao’s wife Jiang Qing, who, as the deputy minister, was put in charge of films at the Ministry of Culture.
Mao was encouraged because of cataracts to cut down on his reading, and to switch to film. Liu was charged with programming and procuring prints for Mao’s private screenings.
Scocca picked the story up from Raymond Zhou in China Daily, but Liu’s account was first published in November in the Yangcheng Evening News, a major daily out of Guangzhou. It was posted online a few weeks later. Here’s the Chinese, “毛泽东有多迷李小龙?”, and a choppy Google translation, “Mao Was a Bruce Lee Fan?” [It’s remarkable how far Chinese-English autotranslation still has to go. We’re barely at Babelfish levels here.]
Liu says his story is from 1974:
Mao Zedong’s like to watch movies there are several categories: first, the international award-winning film; second film biography, “Abraham Lincoln”, “Napoleon,” he loves; third is like watching garden scenery film, like most British films. Often, Mao heard good movie, the file will be down to watch, watch movies right away, very happy.
. At some point, then, Liu traveled to Guangzhou, and on to Hong Kong, where he had not a little bit of trouble getting prints of Lee’s films, The Big Boss, Fist of Fury and The Way of the Dragon, from the wary movie mogul Sir Run Run Shaw.
Where Mao would watch only a few minutes at a time, taking up to ten days to finish another film, he apparently sat straight through Lee’s movies, and even demanded repeat viewings. Liu was afraid to send the prints back to HK, in case Mao asked to see them again.
The incorporation of Mao into the Bruce Lee fan club, the American-born, Hong Kong-raised, one-quarter German Lee [who is known by his given Cantonese name, Li Jun-fan (李振藩)] was timed with the premiere on CCTV6 of a documentary, “Legend of Bruce Lee,” which debuted at Beijing University. It all serves to retroactively position Lee as an inspiring, nationalistic hero of all Chinese, including the Mainland, where he was unknown during his lifetime.
And it all makes me wonder what was actually going on film-wise in the PRC during the tumultuous waning days of Mao’s rule. Because there are some contradictions and gaps in Liu’s story as it’s reported:
Wikipedia, which has the only actual date I can find so far, says Liu was installed as Deputy Culture Minister in February 1976.
Jonathan Clements’ 2006 biography of Mao dates the cataracts to 1974, but also says that Mao was nearly blind, and his slurred speech could only be decoded by his nurse.
As Reeve Wong pointed out to China Daily, Bruce Lee’s films were actually produced by Shaw’s rival studio, Golden Harvest. It’s not clear how or where, but Liu still insists that he got the prints from Shaw.
Given the difficulty in tracking down prints of Hong Kong’s most popular films, I have to wonder what “international award-winning films” and biopics Liu was able to get his hands on. I mean, was there a copy of John Ford’s 1939 film Young Mister Lincoln laying around a cinema after the Revolution?
And the big question, did he watch Michelangelo Antonioni’s epic 1972 documentary Chung Kuo? Antonioni originally shot Chung Kuo/ Cina as a left-to-left cultural gift, with Communist Party participation and supervision. After it came out, though, Madame Mao & her cinematic comrades denounced spectacularly as a capitalist reactionary insult to the Motherland.
A lengthy bio of Liu Qingtang at hudong.com says that in 1976 as the Gang of Four maneuvered for post-Mao power, Minister Liu personally oversaw the production of three “hit films,” Back [反击]、Grand Festival, [盛大的节日], and Fight [搏斗] which attacked Deng Xiaopeng.
After Deng regained and consolidated power and began undoing the effects of the Cultural Revolution, Liu followed the Gang of Four into public disgrace, trial and jail. But he’s apparently out now, and doing fine, if not quite keeping his dates and titles straight.
The Ultimate Collector’s Book Of The Millennium
We go to History with the culture we have, not the culture you want, or might wish to have at a later time.

316 pages. 136 Mb PDF download. Not including the copyright notices, well under 1,000 words.
I can’t quite put my finger on why, but I feel that, at least when The Future looks back on us, here, in this moment, in this culture, in the–as the flight attendant unexpectedly put it when he announced our arrival at Schiphol–in this, the 2,010th Year of Our Lord,
the instruction manual for the 5,000+piece Lego Set 10179-1: The Ultimate Collector’s Millennium Falcon may just end up as the touchstone, the most meaningful book, the best we managed to do. It is certainly the pinnacle of something.

During the unboxing, a giddy Amazon customer notes: “The bound instruction book weighs almost as much as the completed model! Almost. It’s huge!!!”

Seriously, I’m thinking it should be sold as a stand-alone. On the shelf next to The 9/11 Commission Report. And published in a limited edition art book version, on archival paper. Or at least given a fighting chance by being uploaded onto blurb.com.
I mean, it’s allowed, right?
If you plan to print the building instruction, please be sure to download the correct version:
# Building instructions labeled “NA” or “V39” may be printed on US standard letter size paper (8½ in × 11 in, 215.9 mm × 279.4 mm).
# Building instructions labeled “IN” or “V29” may be printed on EU standard A4 paper (210 mm × 297mm, 8.3 in × 11.7 in.)
http://cache.lego.com/bigdownloads/buildinginstructions/4525430.pdf [via things magazine, so this might be the A4 formatted file, fyi]
UPDATE: Lego does have the Instruction Manual available for sale separately. It is $53, plus shipping. [lego.com]
William Lamson At Pierogi Boiler
“…how, slowly and patiently, Mr. Lamson, wearing welder’s goggles, moves his drawing machine along.”
William Lamson‘s show at The Boiler, “A Line Describing The Sun,” got a nice review from Ken Johnson in the Times today.
The 2-channel video of the making of is pretty awesome.
So What Are You Up To Thursday Night?
While I’ve mentioned it on my Twitter feed–the 500 people who read this blog are the same 500 who follow me there, right? @CheapDrugs4U?–I should say here, too, that I have been invited by the folks at 24|7 Creative, a Facebook group sponsored by HP and Intel, to guestpost some of my favorite art, video, and video art picks on their wall.
This is in a run-up to the Big Event this Thursday, some live coverage of the [also HP and Intel-sponsored] YouTube Play blockbuster/extravaganza/show/event at the Guggenheim. So stay tuned, because while my mother did raise me to be a gracious guest, the 24|7 Creative folks are certainly not paying me enough to sway my opinions on anything.
If you haven’t decided whether or not you’ll be attending the YouTube Play gig, and your current lack of tickets is a factor in your decision, then hop on over to this comment contest, where you can win a free pair of tickets to this sure-to-be-landmark spectacle.
I tell you, though, it’s not a slam dunk. Because holy smokes, Thursday at 6:30 is the only scheduled screening so far at the Film Society at Lincoln Center for Sasha Waters Freyer’s new documentary, Chekhov for Children, which tells the incredible-sounding story of Phillip Lopate’s 1979 quest to to a Broadway staging of “Uncle Vanya” with a cast made up entirely of New York City 5th and 6th-graders. Including the filmmaker herself. :
Using incredibly rare archival video and super 8mm student-made films and videos, Chekhov for Children explores the interplay between art and life for a group of students across 30 years–including the filmmaker. It is a rare document of its time that meditates upon the reckoning that comes with middle age through the very moving lens of universal themes: first love, mentoring, and parenting.
I’m getting a little verklempt just typing about it.
The Enlarged Pictures Generation: Alvar Aalto’s 1939 Finnish Pavilion
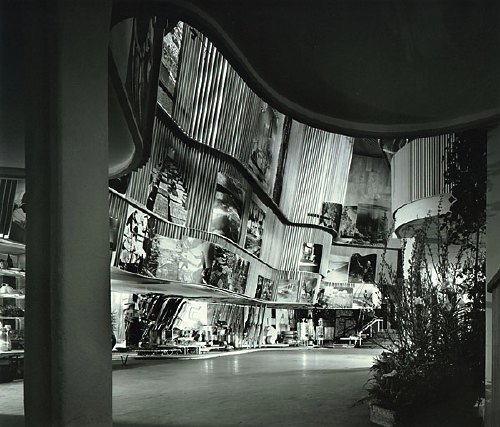

image: vintage silver gelatin print, signed, Ezra Stoller, 1939, via morehousegallery
Do turning back another chapter or two in the history of enlarged pictures, photomurals, and photomontages, where do they turn up the most [besides/before the Museum of Modern Art]? Expos and World’s Fairs. Even more than dioramas, and like the grand cyclorama paintings of earlier eras, giant photos were used by architects–in the service of governments and companies–as modernist, machine age, marketing, mass communication, and propaganda. They were basically highly credible-looking billboards.
None of which is necessarily a bad thing in itself, of course. It’s interesting to note, though, who was creating and using them, because for the most part, it was not artists.
Alvar Aalto’s Finnish Pavilion at the 1939 World’s Fair in New York turns out to have been a stunning and especially instructive example of enlarged photos integrated with modernist architecture. That’s it up top in a photo by –let’s just say I could just as easily title this whole series, “Everything I Know About Photomurals, I Learned From Ezra Stoller.”
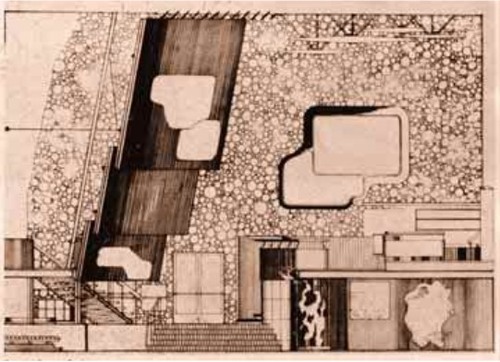
In a plain, rectangular building, Aalto wrapped a second floor exhibition space with an undulating wood-slatted wall, inset with three rows of giant photos [Aalto’s section plan above, via domus, I think] to create a dramatic, infotaining, 52-foot high atrium. A mezzanine restaurant [below] allowed for closer viewing of the photos, which showed, from top down, “Country,” “People,” and “Work,” which culminated, naturally, in the bazaar of real Finnish products underneath.

And what’s that box up there hanging dramatically off the wall, besides the key to the photomurals’ media context and appeal? It’s a projection booth. Films, presumably on the subject of Finland’s awesomeness, were projected onto the atrium wall above the exit. I can’t help but see the effectiveness and popularity of large-scale photos as inextricably driven by architects’ attempt to harness the modern media magic of the cinematic experience. And as antecedents for the now-ubiquitous, immersive projection and installation art works. Like steampunk Pipilotti Rist.
1939 Finnish Pavilion info [designboom]
This Horse-Drawn Corn Picker Is A Thing Of Beauty
From about 44 minutes into John Ruth’s 1975 TV documentary, The Amish: A People of Preservation comes this picture of a horse-drawn, single-row corn picker in what looks like galvanized steel:

It’s about right here that the sculptural beauty of this machine–I do believe it’s a Dearborn-Wood Bros. single-row corn picker, perhaps a precursor to those designed by Clarence Richey and John O’Donnell in 1956 after Ford bought in the company–starts to sink in:

And as soon as you’re caught up in the unexpectedly futuristic, asymmetrical, jet wing-like, origami-like form,

it’s gone.
On another note, the Amish in 1975 appear to have been a lot less self-conscious about cameras in their midst. I blame Witness.
The Amish: A People of Preservation [folkstreams.net]
La Dolce Book Trailer
Wow, if I didn’t worry the ghost of Fellini would come back and smack me upside the head, I’d say the book trailer for Chris Lehmann’s Rich People Things is the The Bicycle Thief of book trailers.
Instead, let’s go with, “It’ll make you say, ‘Hitler in a bunker who?'” That’ll fit on a marquee, won’t it?
Fumis de L’UX
The only word I can think of is the one Things already used: epic.
Sean Michaels goes long and deep for a Brick Magazine profile of the not quite invisible, not quite underground world of L’UX, Untergunther, La Mexicaine de Perforation, the culturebusting, space-infiltrating collective[s] who built a cinema in the catacombs of Paris, and who surreptitiously restored a giant clock in the Pantheon.
At least those are the activities we know about. Michaels talks at length with Lazar Kunstmann as well as with other urban explorers, to try to map out just what’s going on down there. I can’t say we really know any more than we did, but it’s still fascinating stuff.
I have written a lot about LMDP and Untergunther over the years. In 2004, I interviewed Kunstmann and was the first to publish the screening program for LMDP’s subterranean cinema, l’Arenne de Chaillot.. And when the Pantheon clock story broke, I posted pictures of their awesome Rietveldian crate chairs.
It’s been great stuff and great fun, but I’ve never been under any illusion that I’m breaking news or actually investigating. I’m just asking questions that seem obvious to me, but that other journalists or writers never seemed to ask [like what films would you show in a secret catacomb cinema?], and which Kunstmann and his UX colleagues decide to answer.
Michaels ponders at length the somewhat maddening empirical unverifiability of some of UX’s sensationalistic press coverage:
Kunstmann’s tales, the activities he recounts, the cataphile culture he invokes–it is, [UX chief] Lanso suggests, a fumis. It is smoke. It is the smoke that fills our vision, fills newspaper pages, conceals the group’s true projects and real work.
…
As for what this “real work” is, Lanso will not say. These projects, she underlines, are secret. “Don’t think that I say this against you, or against journalists in general. It’s the same for everyone. To be able to do what we do, this is how it has to work.”
I have reached a dead end. Lanso’s secrets are tantalizing, but I can neither confirm nor deny them. UX’s deepest riddles cannot be Googled. The question I ask is, Do I believe them? And then I ask, Do I want to believe them? And then I know my answer.
One thing I DO know for sure, I missed the debut of Kunstmann’s book last year. La Culture Clandestins, L’UX, which I now just ordered from Amazon.fr. Stay tuned.

The Lizard, the Catacombs, and the Clock: The Story of Paris’s Most Secret Underground Society by SEAN MICHAELS, Brick, Summer 2010, Vol 85. [brickmag via things]
Buy La culture en clandestins : L’UX [amazon.fr]
Mark Leckey’s In A Long Tail World @ICA
Last October, Mark Leckey presented In A Long Tail World at the ICA in London. From the writeups, it sounded like a cross between Chris Anderson, Joseph Beuys, Ted by way of the Guggenheim Las Vegas.
Leckey’s now loaded the whole thing onto YouTube, in six parts. Though he’s got a big, Laurie Anderson-y screensaver of an ending, my favorite segment is probably part 1, above. It includes both Leckey’s re-enactment of the earliest TV broadcasting experiment [a recap of his 2007 work, Felix Gets Broadcast] and his quotes from Charles Sirato’s Dimensionist Manifesto from 1936 which posited a new, dematerialized art with humans at the center.
If Leckey didn’t quite make the case that the Long Tail was the fulfillment of Sirato’s vision, it at least crossed its path. And it’s a good watch. [via gavin brown’s (!) blog]
All The Vermeers In New York

A little-known, early Vermeer, the CC145 Concrete Cutter, was apparently on exhibit on Bleecker St this week.
@averybrooks’ twitpics]
Vermeer CC155 [vermeer.com]
Gareth Long’s Untitled (Stories)
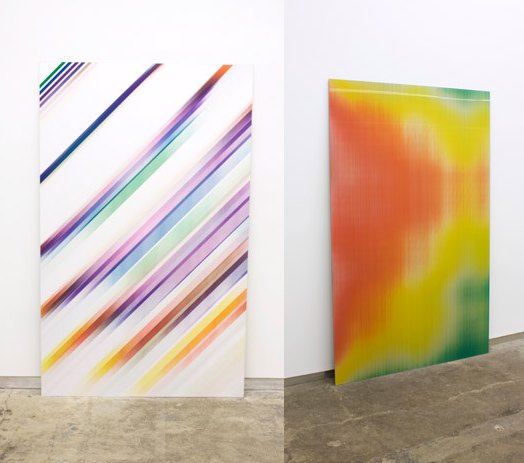

Gareth Long’s giant lenticular prints based on the iconic-yet-anachronous 1991 cover designs for JD Salinger’s books are freaking me out right now.
They’re like Noland or Morris Louis canvases, reanimated through some immediately dated, retrofuturistic technology. Something an aesthete in an early Star Trek movie might have had hanging on his wall. Jeremy Blakes that still work in a blackout.
Which is why they freak me out so much. A Color Field painting hangs unobtrusively, even decoratively, on the wall. A Blake requires turning it on and watching it. You can’t work with those things on in the background, any more than you could sleep with the Flavin on.
Long’s lenticulars thwart all that passive/active viewing negotiation by always being on. If they’re in the room with you, you can’t not look at them.
Go ahead, try it. They’re on view through next weekend at Kate Werble Gallery on Vandam St.
Above: Untitled (Seymour) is the most Salinger cover-esque, while Untitled (Zooey) is the most unabashedly psychedelic. Both images are from Long’s site, where he also offers video clips of the pieces.
Colby Chamberlain ties this “restless” aspect to Salinger in his Artforum review [artforum]
Untitled (Stories) [garethlong.net]
Primary Atmospheres at David Zwirner

Last month I watched the essentially sculptural process of designing and making fiberglass Eames chairs, and I wondered “how design and art ever stayed separate in those days.”
The answer, of course, was that it didn’t. David Zwirner just opened “Primary Atmospheres: Works from California 1960-1970,” the kind of show I’d totally expect to see in a museum [1] [2]. From the press release:
While most of the artworks included in the exhibition can be referred to as minimal in form, their seductive surfaces, often madeout of nontraditional materials, and their luminescent use of color and light characterize them as uniquely Southern Californian.
…
The works on view capture some of the more specific aesthetic qualities of the Los Angeles area during the1960s, where certain cutting-edge industrial materials and technologies were being developed at that time. Many of the artists employed unconventional materials to create complex, highly-finished and meticulous objects that have become associated with the so-called “Finish Fetish” aesthetic.
These artists were also influenced by the industrial paints applied to the surfaces of surfboards and cars, as well as the plastics of the aerospace industry.
Industrial and commercial materials and processes, surfboards, cars, signs, aerospace. As awesome and long-overdue as Zwirner’s show is, it sounds like there’s a lot more about the relationship of postwar art and design to be discovered, written about, and shown. So hop to.
Primary Atmospheres: Works from California 1960-1970, through Feb. 6, 2010 [davidzwirner.com]
16miles reports beautifully from the scene of the opening [16miles.com]
image above: works by Craig Kaufmann in vacuum-formed plexi; Larry Bell in mineral coated glass; and De Wain Valentine in fiberglass-reinforced polyester, via zwirner.
[1] In fact, it feels like a slice of the Pompidou’s much larger 2006 survey of Los Angeles, hopefully without the negligent destruction of the non-traditionally constructed art. Several of these artists were also in PS1’s odd “1969” show last year, so not quite as unexposed as the press release implies.
[2] Zwirner’s last Flavin show was the same museum-quality, but not to be found in a museum. And then there was the Flavin Green Gallery and Kaprow shows at Hauser & Wirth. How are there not more museums in town doing small-to-medium-sized, historical contemporary shows like this? The exhibition equivalent of an essay instead of a book? It seems like such a free way to work and think. PS1 is the closest I can think of, though I’m always ready to believe I just don’t get out enough.
