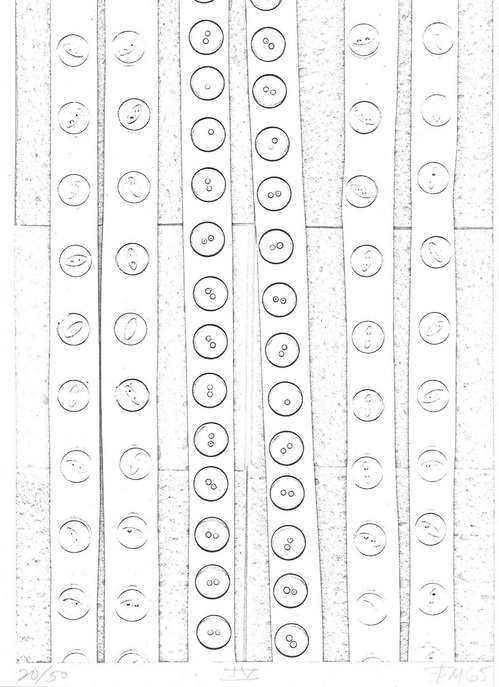
Illustration from Ed Meneeley’s Tender Buttons, 1964
You may know Edward Meneeley from such art historical blog posts as, “The guy who published the subscription art slide library and newsletter which Rauschenberg refused to allow to reproduce Short Circuit in 1962 because of the agreement Rauschenberg and Johns had come to after their messy breakup,” and “The guy who told me how Johns really transformed an erased de Kooning drawing into Erased De Kooning Drawing,” and “The guy who was hooking up with at least Bob at the time, yow, small world.”
But he also turns out to be one of the first artists to use the then-new technology of photocopying to make prints. Starting in 1964, when a friend took him to IBM’s offices, where he saw a copy machine for the first time.
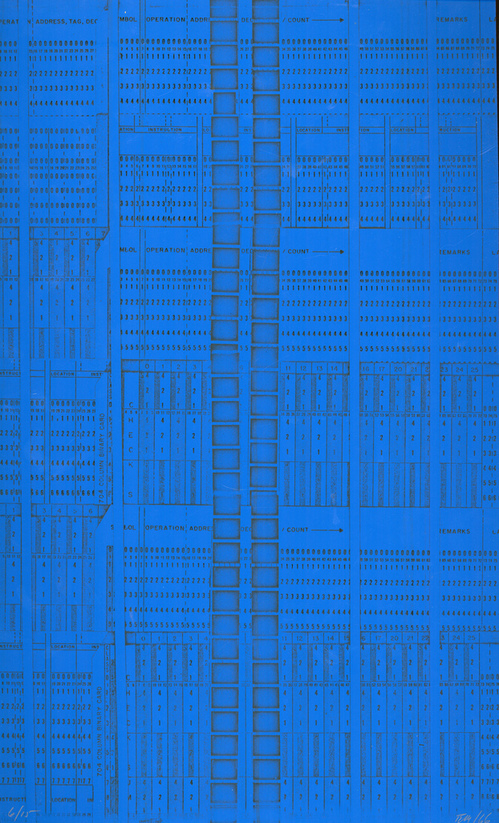

Edward Meneeley, IBM Drawings
Meneeley made three print portfolios using a photocopier: Tender Buttons (1965) [top] was a suite of illustrations for Gertrude Stein’s work of the same name. IBM Drawings (1966) was an exploration of the medium and its context, abstract, collaged images composed from computer tapes and other office ephemera that Meneeley found at hand. There was also a hairy, photocopied butt, presumably the artist’s.
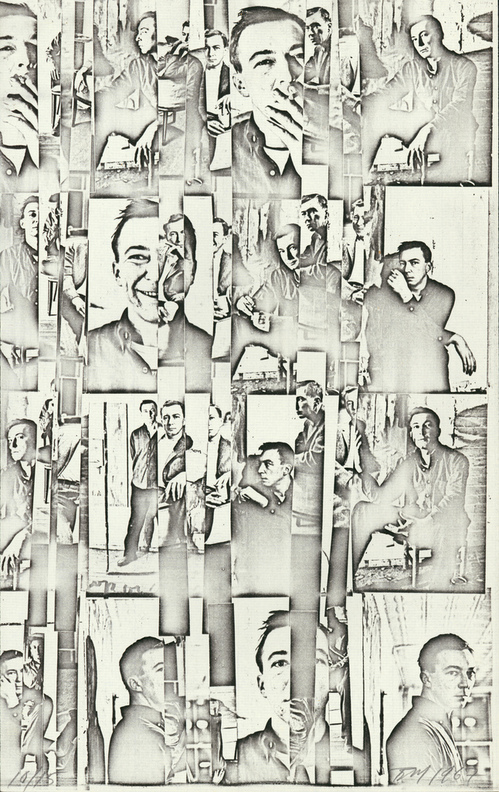

And then in 1968, the year Seth Siegelaub instigated his highly influential, photocopied-book-as-exhibition project, The Xerox Book, Meneeley made Portraits: People and Objects, which included a reassembled photo collage portrait of his friend Jasper Johns. But where Siegelaub and his crew were skewing to the conceptual aspects of copying, Meneeley was very attuned to the technical subtleties of photostatic reproduction, which he interpreted as a unique printmaking medium, an updated form of lithography.
Great stuff.
Edward Meneeley and the advent of the electrostatic artist’s print [rectoversoblog, which has many more images, not just the 2nd & 3rd images above]
Skip to content
the making of, by greg allen
