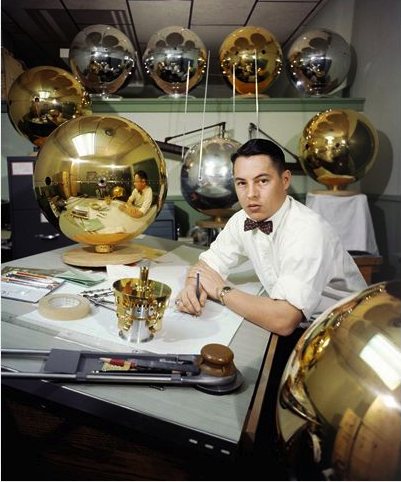
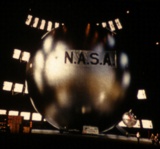
I could feel Mondo-Blogo was baiting me as I scrolled through the photos from MoonFire, Taschen's luscious 2009 commemorative book for the anniversary of the Apollo 11 landing. He was amped about the text by Norman Mailer, and the multiple insane limited edition versions of the book--with or without embedded lunar asteroid fragments and lander-style display cases--designed by Marc Newsom. I, meanwhile, was sensing some ur-satelloon spheres coming on, and--BOOM. This photo above.
But what was it? I couldn't tell the mission, and I couldn't find the same or similar images of such Sputnik-like satellites in progress, no matter how hard I Googled. And from the preview, neither Mondo nor I could read the captions. The trade edition of the book wasn't out yet, at least in the stores--and space bookshops, and the National Air and Space Museums--I visited last week. What to do? I asked Taschen's publicist for help, and voila. Project Vanguard.
This is a previously unpublished 1957 image from LIFE Magazine photographer Hank Walker of the Project Vanguard team at the Naval Research Laboratory, hard at work on the world's first "earth satellite." [Well, not quite the first, as it turned out.] But almost no one in the US knew about Sputnik on June 3rd, 1957 when LIFE ran an excited cover story about Vanguard's development ["Man-Made Moon Takes Shape," "Shell of Satellite Mirrors its Makers"] That's Vanguard scientist Alexander Simkovich, by the way.

Walker's other LIFE photos of Project Vanguard from the Spring of 1957 are just as awesome. Some of the most artistic highlights:
The crating: Apparently, at least 35 Vanguard and Vanguard II satellite shells were manufactured in Detroit by Brooks & Perkins, then shipped to Washington for assembly. I have to wonder what Eva Hesse was doing while these things were being packed:

The see-through model: Instead of an internal sphere full of scientific instruments, the 20-inch Vanguard II satellites were designed with a suspended, miniaturized, stacked core, as this plexiglass model showed:
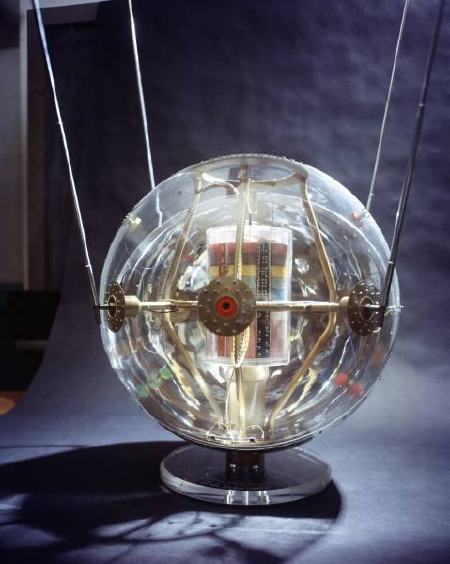

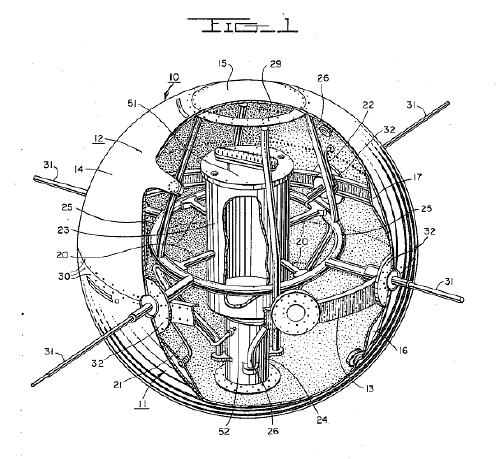
This looks remarkably like the cutaway drawing for the first patent ever issued for a satellite structure. Satellite team leader Robert C. Baumann filed the patent in August 1957, and it was granted in 1958. In the mean time, of course, the Soviet Union had launched two Sputniks and the rocket carrying the first, grapefruit-sized Vanguard satellite, had exploded on the launch pad on live television [that satellite was recovered intact and is on view at the Air & Space Museum, btw]:
The making of: Brooks & Perkins manufactured the vanguard shells from sheets of magnesium [below], then plated them with gold. A remarkably detailed Time Magazine article from April 15, 1957 explains the rest of the manufacturing process:
When the satellites came from their manufacturer, Brooks & Perkins, Inc. of Detroit, they were thin-skinned magnesium spheres plated with gold. Aluminum is better for reflecting sunlight, but since aluminum will not stick to gold, the gold had to be covered with a thin film of chromium. Aluminum will stick to chromium, but it also mixes with it and loses part of its reflecting power. So the chromium film in turn had to be coated with glassy silicon monoxide, and then with aluminum.The delicate work of depositing the coatings was done by the Army Engineers at Fort Belvoir, Va. Each satellite was put in a vacuum chamber and turned, like a chicken on a spit while the materials in the coatings were evaporated electrically and deposited on its surface. The final coat was a second layer of silicon monoxide.

In terms of the Space Race, Project Vanguard was only a fair success, and it was quickly superseded. A Vanguard II satellite launched in 1958 is currently still in orbit and is the oldest man-made object in space. So that should mean that at least a couple dozen of these iridescent masterpieces still roam the earth--or are stuck in crates in NASA scientists' grandchildren's garages waiting to be liberated and exhibited. The search is joined.
Oh, look, here's one that's off the list: a 1958 Vanguard Lyman Alpha replica or flight spare on display at the National Air & Space Museum's Udvar-Hazy site at Dulles.